Rudrakshi Sharma, a second-year student at Symbiosis Law School, Noida has written this article. “The Role of the Speaker of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.”
Introduction
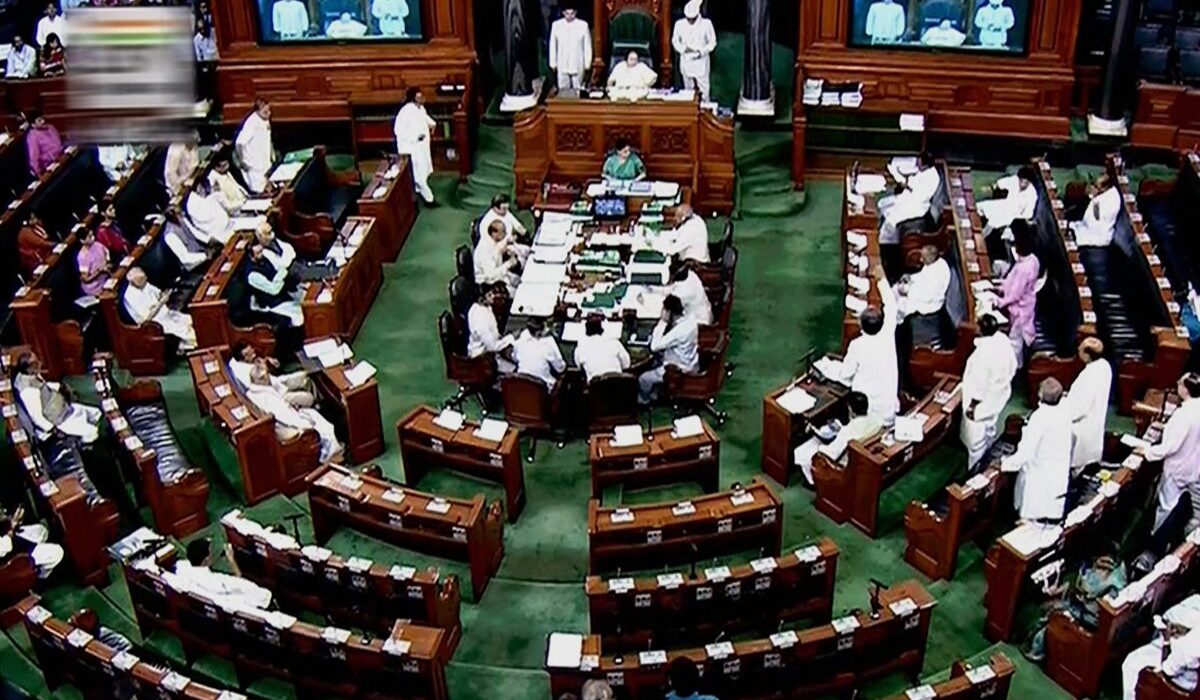
The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha plays a crucial role in maintaining order and discipline in the Indian Parliament. As the presiding officers of the two houses, they are responsible for conducting the proceedings of the houses and ensuring that they are conducted in an orderly and disciplined manner. They are also responsible for upholding the parliamentary conventions and procedures and protecting the members’ and houses’ rights and privileges. In this article, we will discuss the role of the Speaker of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha in Parliament.
The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha are elected by the members of their respective houses and must be elected members. They are elected for a term of five years (Speaker) and six years (Chairman), respectively, or until the dissolution of the House, whichever is earlier. The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha holds a pivotal position in the parliamentary democracy of India, and their role goes beyond just conducting the proceedings of the houses. They have the power to maintain order and decorum in the houses, decide on the admissibility of questions and motions, certify Bills passed by the houses, and act as the custodian of the privileges of the houses. Let us dive into the details of their role in the Indian Parliament.
Speaker’s Role in Parliament
The Parliament of India is the country’s supreme legislative body and comprises two houses: the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha. The Speaker of the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha Chairman are the respective houses’ presiding officers. He is pivotal in maintaining the decorum and smooth functioning of the Houses.
The Speaker of Lok Sabha has a crucial role in India’s parliamentary system. As the presiding officer of the lower House, the Speaker is responsible for conducting the proceedings of the House, maintaining order and decorum, and ensuring that the business of the House is conducted fairly and impartially. The Speaker is also responsible for interpreting and enforcing the rules of procedure of the House, deciding on the admissibility of questions and motions, and certifying Bills passed by the House. The Speaker also has the power to convene joint sittings of both houses of Parliament in case of a deadlock between the two houses. Additionally, he also has the responsibility of safeguarding the rights and privileges of the members of the House.
The Lok Sabha Speaker
The Speaker of the Lok Sabha is the highest officer of the House and is responsible for conducting the proceedings of the House. He is elected by the members of the Lok Sabha from amongst themselves. The Speaker is required to be an elected member of the House and is elected for five years or until the dissolution of the Lok Sabha, whichever is earlier.
The Speaker of the Lok Sabha has several vital functions, including:
- The Speaker is responsible for ensuring that the proceedings of the Lok Sabha are conducted in an accurate manner. The Speaker can adjourn the House or suspend a member for disorderly conduct.
- The Speaker is responsible for maintaining order and decorum in the House. The Speaker can take disciplinary action against members who breach the rules of the House.
- The Speaker decides on the admissibility of questions, motions, and resolutions brought before the House. The Speaker’s decision on the admissibility of any matter is final.
- The Speaker is responsible for certifying Bills passed by the House before they are sent to the President for assent.
- The Speaker is the custodian of the privileges of the House. He is responsible for protecting the rights and privileges of the members and the House.
- The Speaker represents the House in its dealings with other government institutions, such as the Executive and the Judiciary.
The Rajya Sabha Chairman
The Chairman of the Rajya Sabha is the presiding officer of the House and is elected by the members of the Rajya Sabha from amongst themselves. He is required to be an elected member of the House and is elected for six years.
The Chairman of the Rajya Sabha has several vital functions, including:
- The Chairman is responsible for ensuring that the proceedings of the Rajya Sabha are conducted in a proper manner.
- The Chairman can adjourn the House or suspend a member for disorderly conduct.
- The Chairman is responsible for maintaining order and decorum in the House. The Chairman can take disciplinary action against members who breach the rules of the House.
- The Chairman decides on the admissibility of questions, motions, and resolutions brought before the House. The Chairman’s decision on the admissibility of any matter is final.
- The Chairman is responsible for certifying Bills passed by the House before they are sent to the President for assent.
- The Chairman is the custodian of the privileges of the House. He is responsible for protecting the rights and privileges of the members and the House.
- The Chairman represents the House in its dealings with other government institutions, such as the Executive and the Judiciary. In addition to their formal functions, the Speaker and the Chairman also have informal roles as mediators.
Legal Provisions Standpoint
The legal provisions regarding the role of the Speaker and the Chairman are enshrined in the Constitution of India. Article 93 of the Constitution provides for the Speaker of Lok Sabha, while Article 94 provides for the Deputy Speaker. Article 94 also lays down the procedure for the election of the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker. Similarly, Article 96 provides for the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, while Article 97 provides for the Deputy Chairman. Article 97 also lays down the procedure for the election of the Chairman and the Deputy Chairman.
Under the Constitution, the Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha has certain powers and privileges. They are empowered to maintain order and decorum in the houses and are responsible for business in their respective houses. They also represent the houses in their dealings with other institutions of government. The Speaker and the Chairman are elected by the members of their respective houses. They hold a position of great responsibility in the parliamentary democracy of India.
In addition to the Constitution, the role of the Speaker of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha is also governed by the rules of procedure and conduct of business in the houses. The rules of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha provide for the powers and duties of the Speaker and the Chairman. It includes the conduct of proceedings in the houses, the maintenance of order and decorum, and the interpretation and enforcement of the rules of procedure. The rules also provide for the procedures for the election and removal of the Speaker and the Chairman. These legal provisions help to ensure that the Speaker and the Chairman discharge their duties fairly and impartially and uphold the principles of parliamentary democracy.
Election and Tenure of the Speaker of Lok Sabha
The Constitution of India and the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha govern the election and tenure of the Speaker of Lok Sabha. According to Article 93 of the Constitution, the Speaker is elected by members of the Lok Sabha from among themselves and must be a member of the House. The election of the Speaker is presided over by the Pro term Speaker, whom the President of India appoints for this purpose. The Pro tem Speaker is usually the senior-most member of Lok Sabha. Once the Speaker is elected, the Pro tem Speaker ceases to hold office.
The life of the Lok Sabha determines the tenure of the Speaker. However, if the Lok Sabha is dissolved before the completion of its term, the Speaker continues to hold office until the first meeting of the newly constituted Lok Sabha. The Speaker can be removed from office by a resolution passed by a majority of the members of Lok Sabha. The resolution must be supported by at least one-fourth of the total number of members of the Lok Sabha. The Speaker can also resign from his/her office by submitting a written resignation to the Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha.
Election and Tenure of the Chairman of Rajya Sabha
The Chairman of Rajya Sabha is elected by the members of the House from amongst themselves. According to Article 64 of the Constitution of India, the Vice President of India serves as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. In the absence of the Vice President, the Deputy Chairman presides over the proceedings of the House.
The election of the Chairman takes place at the beginning of the first session of Rajya Sabha following a general election or whenever the office becomes vacant. The election is conducted by the Secretary-General of Rajya Sabha or any other officer nominated by the President of India. The Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Rajya Sabha guide the election process.
The Chairman of Rajya Sabha holds office for a term of six years. However, the Chairman may resign from his/her office by submitting a written resignation to the Deputy Chairman of Rajya Sabha. The Chairman may also be removed from office by a resolution passed by the Rajya Sabha with most of its members present and voting. The resolution must be supported by not less than two-thirds of the members present and voting.
Powers of the Chairman of Rajya Sabha and Speaker of Lok Sabha in Maintaining Order in the House – A Comparison
The Chairman of Rajya Sabha and Speaker of Lok Sabha have important roles in maintaining discipline in their respective Houses. The key powers of both the Chairman and Speaker are to regulate the conduct of members during the proceedings. Both the Chairman and Speaker have the power to expunge any words that are deemed unparliamentary or derogatory. Another common power of the Chairman and Speaker is to maintain the order of business in the House. This includes deciding which items of business are taken up for discussion, allotting time for speeches, and ensuring that the business of the House is conducted efficiently. Both the Chairman and Speaker can also adjourn or suspend the sitting of the House if the circumstances so warrant.
However, there are also some differences in the powers of the Chairman and Speaker. For example, the Speaker of Lok Sabha has the power to certify a Bill as a Money Bill. Whereas, the Chairman of Rajya Sabha does not have this power. Additionally, the Chairman of Rajya Sabha has the power to determine whether a Bill is a Money Bill or not, while the Speaker of Lok Sabha does not have this power.
In conclusion, while there are similarities in the powers of the Chairman and Speaker, there are also some differences. These powers are guided by the Constitution of India, the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in the Houses, and parliamentary conventions and traditions. Understanding these powers is important to ensure that the business of the Houses can be conducted smoothly and efficiently.
Key Facts Regarding The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha
- The first Speaker of Lok Sabha, Ganesh Vasudev Mavalankar, was elected on May 15, 1952. He served as the Speaker for the first two Lok Sabha until his death in 1956.
- The Chairman of the Rajya Sabha is the highest-ranking official in the Parliament. He is ranked fourth in the Indian order of precedence, after the President, Vice President, and Prime Minister.
- The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha has the power to cast a deciding vote in the event of a tie during voting in their respective houses.
- The Speaker of Lok Sabha is also the ex-officio Chairman of the Indian Parliamentary Group, an organization that promotes parliamentary diplomacy and international relations.
- The Chairman, like the Vice President of India, serves as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha TV channel.
- In 1953, the then-Speaker of Lok Sabha, Mavalankar, made an unprecedented decision to allow the leader of the opposition, A.K. Gopalan, to speak for more than an hour, despite objections from the ruling party. This set a precedent for the fair and impartial conduct of the Speaker in Parliament.
- The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha have their own official residences, which are provided by the government.
- The Chairman of the Rajya Sabha is also responsible for conducting the swearing-in ceremony of the President of India.
- The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha is addressed as “Speaker Sir” and “Honourable Chairman,” respectively.
- The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha is responsible for ensuring the safety and security of the members of their respective houses during parliamentary proceedings. They have the power to order the removal of any member. If in case anyone violates the rules of the House or disturbs the proceedings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of the Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha is critical in Parliament. They play a pivotal role in ensuring that the proceedings of the houses are conducted in an orderly and disciplined manner and that the parliamentary conventions and procedures are adhered to. They also act as the custodians of the privileges of the members and the houses. Both the Speaker and the Chairman represent the houses in their dealings with other institutions of government. The Speaker and the Chairman are elected by the members of their respective houses. They hold a position of great responsibility in the parliamentary democracy of India. It is through their efforts that the Indian Parliament remains one of the most effective legislative bodies in the world.
The role of the Speaker of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha is vital to the functioning of the Indian Parliament. As per the legal provisions outlined in the Constitution and rules of procedure of the respective houses, the Speaker and the Chairman have been entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining order and decorum in the houses, conducting business in a fair and impartial manner, and upholding the principles of parliamentary democracy. The legal provisions provide them with the necessary powers and privileges to carry out their duties effectively. They play a critical role in ensuring the smooth functioning of the Indian Parliament. The Speaker of Lok Sabha and the Chairman of Rajya Sabha are key figures in the Indian political system, and their impartiality and integrity are crucial to the effective functioning of the democratic institutions of India[1].
Also Read: Legislative Relations Between Union & State
[1] Representation Of The People Act 1951 | Simplified UPSC. https://simplifiedupsc.in/representation-of-the-people-act-1951/
![]()





Leave feedback about this